The global market for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) is expected to grow from $27 billion in 2022 to $83 billion by 2030, a staggering 12% annual growth rate. This remarkable statistic underscores the crucial role ADAS plays in enhancing vehicle safety and preventing accidents on our roads.
ADAS functionalities can significantly impact the driving experience, with research showing a 27% reduction in bodily injury claim frequency and a 19% reduction in property damage frequency for ADAS-equipped vehicles. These advanced systems, which integrate a range of sensors, cameras, and sophisticated software, provide real-time assistance to drivers, mitigating risks and reducing the likelihood of collisions.
Key Takeaways
- ADAS technologies, including features like adaptive cruise control, lane departure warning, and automatic emergency braking, are becoming increasingly common in modern vehicles.
- These systems can significantly enhance driver safety, with research indicating a 27% reduction in bodily injury claims and a 19% reduction in property damage claims for ADAS-equipped vehicles.
- The global ADAS market is expected to grow rapidly, from $27 billion in 2022 to $83 billion by 2030, highlighting the increasing importance of these safety-enhancing technologies.
- ADAS relies on a combination of sensors, cameras, and advanced software to provide real-time assistance to drivers, helping to prevent accidents and mitigate the severity of collisions.
- The continued development of ADAS and autonomous driving technologies has the potential to revolutionize road safety by reducing human error, a leading cause of accidents.
What are Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)?
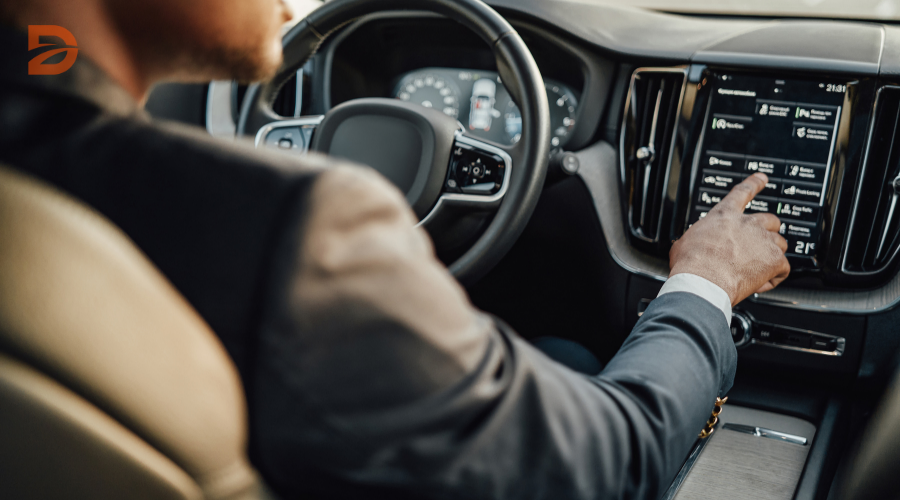
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) are an integral part of the ongoing evolution towards autonomous driving. These comprehensive technologies are integrated into modern vehicles to enhance driver safety and reduce the likelihood of accidents. ADAS systems utilize a variety of sensors, cameras, radar, and sophisticated software to monitor the vehicle’s surroundings and provide real-time assistance to the driver.
ADAS encompasses a wide range of features that work together to mitigate risks and improve overall road safety. These systems rely on sensor fusion, combining data from various sources such as automotive imaging, LiDAR, radar, image processing, and computer vision to make faster and more accurate decisions compared to human drivers.
Key ADAS Features and Their Capabilities
- Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) automatically adjusts the vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe following distance, preventing speed-related accidents.
- Lane Departure Warning (LDW) and Lane Keeping Assist (LKA) monitor lane markings and alert the driver or gently steer the vehicle back into the lane, preventing unintentional lane departures.
- Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) uses sensors to detect potential collisions and can automatically apply the brakes to avoid or mitigate the impact.
- Blind Spot Detection uses sensors to detect vehicles in the driver’s blind spots and provide visual or audible alerts, improving awareness and reducing the risk of sideswipe collisions.
- Parking Assistance and Rear-View Cameras help drivers safely navigate tight spaces and avoid obstacles, particularly in crowded parking lots.
These are just a few examples of the advanced driver assistance technologies that are transforming the driving experience and making our roads safer. As ADAS systems continue to evolve, they are paving the way for the next generation of autonomous vehicles, further reducing the risk of human error and enhancing overall road safety.
| ADAS Feature | Description | Impact on Safety |
|---|---|---|
| Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) | Automatically adjusts vehicle speed to maintain a safe following distance | Reduces the risk of rear-end collisions |
| Lane Departure Warning (LDW) and Lane Keeping Assist (LKA) | Monitors lane markings and alerts the driver or gently steers the vehicle back into the lane | Prevents unintentional lane departures, reducing the risk of side-swipe collisions |
| Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) | Uses sensors to detect potential collisions and can automatically apply the brakes | Helps avoid or mitigate the impact of front-end collisions |
| Blind Spot Detection | Detects vehicles in the driver’s blind spots and provides visual or audible alerts | Improves awareness and reduces the risk of side-swipe collisions |
| Parking Assistance and Rear-View Cameras | Help drivers safely navigate tight spaces and avoid obstacles | Enhances safety in crowded parking lots and during reversing maneuvers |
Key Features of ADAS and Their Impact on Safety
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) encompass a wide range of technologies designed to enhance driver safety and prevent accidents. From adaptive cruise control to blind spot detection, these cutting-edge features play a crucial role in making our roads safer. Let’s explore some of the key ADAS components and their remarkable impact on accident prevention.
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC)
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) can reduce rear-end collisions by up to 42%, primarily due to its ability to react quicker than human drivers in emergency situations. By maintaining a safe following distance and automatically adjusting speed, ACC helps mitigate the risk of collisions caused by sudden stops or changes in traffic flow.
Lane Departure Warning & Lane Keeping Assist (LDW & LKA)
Lane Departure Warning (LDW) and Lane Keeping Assist (LKA) systems play a crucial role in accident prevention. Research shows that these technologies can reduce fatality accidents by 86% and lower the chances of injury-causing accidents by 24%. By alerting drivers to unintended lane departures and actively assisting in lane-keeping, these features help reduce accidents caused by driver inattention or fatigue.
Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB)
Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) is a powerful ADAS feature that can lower the chances of a rear-end collision by 50% and reduce accidents involving pickup trucks by 40%. By detecting imminent collisions and automatically applying the brakes, AEB helps mitigate the severity of accidents and prevent them altogether.
Blind Spot Detection
Blind Spot Detection technology makes drivers 14% less likely to be involved in a lane-change accident compared to vehicles without this feature. By monitoring the areas around the vehicle that are typically blind spots, Blind Spot Detection systems alert drivers to the presence of other vehicles, enhancing their awareness and decision-making during lane changes.
Parking Assistance & Rear-View Cameras
Parking Assistance systems, combined with Rear-View Cameras, can reduce parking-related accidents by 42%. By providing enhanced spatial awareness and feedback to drivers, these features help prevent collisions and mitigate the risk of accidents during parking maneuvers.
As ADAS technologies continue to evolve, the impact on accident prevention becomes increasingly significant. Maintaining and updating these systems is crucial to ensure their continued effectiveness in enhancing driver safety and reducing the likelihood of accidents.
Advanced driver assistance systems, ADAS
Advanced driver assistance systems, or ADAS, are an integral part of the broader movement towards autonomous driving. These cutting-edge technologies equip vehicles with the ability to perform an array of tasks independently, further enhancing safety by minimizing human error, a leading cause of accidents on the roads.
ADAS systems rely on a combination of sensors, cameras, radar, and sophisticated software to provide real-time assistance to drivers, helping to mitigate risks and reduce the likelihood of collisions. From adaptive cruise control and lane departure warning to blind spot detection and automated emergency braking, these advanced features work in tandem to create a safer driving experience.
- Radar sensors use radio waves to detect the position, speed, movement, and size of objects, enabling Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) and collision avoidance.
- Ultrasonic sensors emit sound waves to measure proximity to objects, assisting with parking assistance and obstacle detection.
- Cameras capture visual information for functions like Lane Departure Warning (LDW), traffic sign recognition, and pedestrian detection.
- Sensor fusion integrates data from multiple sensors using Electronic Control Units (ECUs) for a comprehensive understanding of the environment in real-time.
The impact of ADAS on vehicle safety is undeniable. Collision Avoidance Systems (CAS) help prevent collisions by sending warnings to drivers and automatically initiating braking, while Lane Departure Warning (LDW) systems use image processing and pattern recognition to detect unintentional lane drifts. Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) and Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) further enhance safety by automating speed adjustments and providing alerts for vehicles in blind spots.
As advanced driver assistance systems continue to evolve, their role in making vehicles safer and smarter becomes increasingly vital. ADAS technology plays a key part in accident prevention, contributing to a significant reduction in the occurrence of accidents caused by human error. The future of vehicle safety lies in the continued development and integration of these cutting-edge systems.
ADAS Systems’ Effectiveness in Accident Prevention
Research has shown that advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and insurance claims. These cutting-edge technologies, which include features like front crash prevention, lane departure prevention, blind spot detection, and rear crash prevention, have demonstrated remarkable effectiveness in enhancing road safety.
According to recent studies, vehicles equipped with both autonomous emergency braking and lane departure warning were 23% less likely to crash compared to those without these ADAS features. Blind spot detection, in particular, was associated with a 14% reduction in crashes after controlling for other ADAS technologies.
The safety benefits of ADAS continue to improve over time as the technology evolves. Newer model vehicles with autonomous emergency braking and lane departure warning were 13% less likely to crash for 2014 models and an impressive 34% less likely to crash for 2017 models. This highlights the growing effectiveness of ADAS in preventing accidents.
The data clearly shows that ADAS features play a crucial role in enhancing road safety and reducing the burden of insurance claims. These advanced systems have the potential to revolutionize the way we approach accident prevention, ultimately leading to safer roads for all.
Legal Implications and Challenges of ADAS
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) have made significant strides in enhancing vehicle safety, but they also present legal implications and challenges that must be addressed. While these technologies contribute to accident prevention, drivers must remain attentive and be ready to take control when necessary, as the systems are not infallible and still have limitations.
One of the primary legal concerns is the maintenance and updates of ADAS systems. Neglecting these crucial aspects can lead to legal complications, as failing to keep the systems working correctly could make them unreliable, potentially resulting in an accident for which the driver might be held responsible. Additionally, ADAS liability is a complex issue, as determining responsibility in the event of an accident involving ADAS can be challenging.
Regulations surrounding ADAS use also vary by jurisdiction, and drivers must comply with all traffic laws and regulations to avoid legal issues. The rapid pace of technological innovation in ADAS requires continuous updates and adaptations of regulations by regulatory bodies, such as the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States, to ensure the safety and reliability of these systems.
Furthermore, ADAS legal implications extend beyond the driver’s responsibility. As these technologies become more autonomous, liability may shift towards manufacturers if the system is found defective, impacting insurance policies and premiums. Regulatory bodies are working to build public trust in ADAS technologies by ensuring clear communication about the benefits, risks, and limitations of the systems.
In conclusion, the integration of ADAS in modern vehicles presents both opportunities and challenges. Navigating the legal landscape of these advanced technologies requires a collaborative effort between drivers, manufacturers, and regulatory agencies to ensure the safety and reliability of ADAS systems.
The Future of ADAS and Vehicle Safety
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, the future of advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) holds immense promise for improving vehicle safety and reducing the number of accidents on our roads. Experts anticipate the continued development of autonomous driving technology, potentially leading to fully autonomous vehicles that could revolutionize road safety by addressing a leading cause of accidents: human error.
According to research, an astounding 94% of U.S. traffic accidents are caused by human error, with recognition errors being the greatest percentage, followed by decision errors, performance errors, and non-performance errors. As ADAS features become more integrated into vehicles, it is essential for drivers to remain informed and vigilant, as even with advanced technology, accidents can still occur, and drivers must be prepared to take control in case these systems fail.
The comfort of consumers with ADAS features such as blind-spot monitoring, lane departure warnings, and parking assistance will facilitate the transition to fully autonomous vehicles. However, it will require a few more years for society and the automotive industry to be fully prepared for the widespread adoption of autonomous cars, as McKinsey estimates that Level 5 autonomous vehicles may not be accessible until at least 2030, with broader adoption to follow over time.
The future of ADAS and vehicle safety is further bolstered by the integration of 5G technology and augmented reality, which will support and enhance ADAS functionalities through improved bandwidth and lower latency. Additionally, the use of sensor fusion, combining multiple sensor types like cameras, lidar, radar, and ultrasonic sensors, allows for more advanced navigation systems that address the limitations of individual sensor technologies.
As more manufacturers adopt ADAS systems, the demand for safety features across the automotive industry is increasing, leading to fewer traffic accidents, reduced traffic congestion, better fuel efficiency, and lower maintenance costs, which can ultimately result in lower insurance premiums. The future of ADAS and vehicle safety holds the promise of a safer, more efficient, and more sustainable transportation system.
Conclusion
Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) are revolutionizing the automotive industry, significantly enhancing safety and preventing accidents on the road. ADAS encompasses a wide range of technologies, from adaptive cruise control and lane departure warning to automatic emergency braking and blind spot detection, all working together to mitigate risks and provide real-time assistance to drivers.
While these systems have demonstrated impressive reductions in crashes and insurance claims, it is essential for drivers to remain vigilant, as ADAS technologies are not infallible and have legal implications that must be understood. As the future of vehicle safety continues to evolve, with the potential for fully autonomous driving, the impact of ADAS on road safety is poised to become even more profound, helping to reduce human error and create a safer driving experience for all.
As the ADAS market continues to grow at a rapid pace, the critical role of semiconductor manufacturers in developing innovative solutions to overcome the challenges faced by these systems cannot be overstated. Reducing weight, and size, and increasing reliability are the main focus areas for these companies, ensuring that ADAS technologies continue to advance and make a significant impact on road safety in the years to come.
FAQ
What are Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS)?
ADAS encompasses a comprehensive set of technologies integrated into modern vehicles to enhance driver safety. These systems rely on a combination of sensors, cameras, radar, and sophisticated software to provide real-time assistance to drivers, mitigating risks and reducing the likelihood of accidents.
What are the key features of ADAS and their impact on safety?
Key ADAS features include Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC), Lane Departure Warning & Lane Keeping Assist (LDW & LKA), Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB), Blind Spot Detection, Parking Assistance, and Rear-View Cameras. These technologies have been shown to significantly reduce the risk of accidents and insurance claims, with front crash prevention systems cutting rear-end crashes in half and lane departure prevention reducing fatality accidents by 86%.
How effective are ADAS systems in accident prevention?
Research has shown that ADAS features like front crash prevention, lane departure prevention, blind spot detection, and rear crash prevention are associated with significant reductions in crashes and insurance claims. For example, front crash prevention systems with automatic braking can cut rear-end crashes in half, while forward collision warning alone reduces them by 27%. Lane departure prevention can reduce fatality accidents by 86% and lower the chances of injury-causing accidents by 24%.
What are the legal implications and challenges of ADAS?
While ADAS technologies contribute significantly to safety, drivers must remain attentive and be ready to take control when necessary, as the systems are not infallible and still have limitations. Neglecting the maintenance and updates of ADAS systems can lead to legal complications, and failing to keep these systems working correctly could make them unreliable, potentially resulting in an accident for which the driver might be held responsible. There are also other legal challenges associated with ADAS-related accidents, such as determining liability, and regulations surrounding ADAS use vary by jurisdiction.
What is the future of ADAS and vehicle safety?
Experts anticipate the continued development of autonomous driving technology, potentially leading to fully autonomous vehicles. These innovations have the potential to revolutionize road safety by reducing human error, which is a leading cause of accidents. As ADAS features become more integrated into vehicles, it is essential for drivers to remain informed and vigilant, as even with advanced technology, accidents can still occur, and drivers must be prepared to take control in case these systems fail.